Objective: We have reviewed the data of the patients in order to evaluate the effectiveness of our ureterocystoplasty technique in augmentation cystoplasty operation.
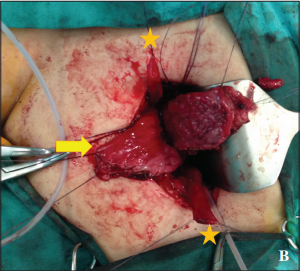
Material and methods: Data of a total of 16 patients with bilateral functional kidneys who had undergone augmentation ureterocystoplasty between January 1995 and June 2018 which were retrieved during the retrospective archive scanning were included in the study. Ultrasonography (USG), serum blood urea nitrogen and creatinine values and Technetium-99 DTPA (Tc-99 DTPA) scan were used to evaluate the renal function of the patients. Intravenous pyelography (IVP) and USG were used to evaluate the ureters before surgery. Magnetic resonance (MR) urographies were performed in our center.
Results: Of the total 16 patients, 10 were male and 6 were female, while ages ranged from 1 to 24 years. Among 16 patients, the most common cause of neurogenic bladder etiology was meningomyelocele. In the urodynamic studies performed before the operation, it was determined that the bladder capacities of the patients were between 40-180 mL and the bladder compliances were 1.0-4.0 cc/cmH2O. At postoperative 3rd months, it was determined that the bladder capacities of the patients were between 180-330 mL and the bladder compliances were between 6.0-24.0 cc/cmH2O.
Conclusion: Augmentation ureterocystoplasty seems to be an appropriate technique in which successful results are obtained with appropriate patient selection. Besides, complications that may occur due to use of ileal segment are avoided.
Cite this article as: Ergin G, Köprü B, Ebiloğlu T, Kibar Y, Dayanç M. Our experience with ureterocystoplasty in bilateral functional kidneys. Turk J Urol 2019; 45(Supp. 1): S78-S83.

.png)
.jpg)
.png)
.png)